- Home
- Work and Invest in EEC
- Labor
- Human Capital Development under the EEC Model
Human Capital Development
under the EEC Model
Human Capital Development
under the EEC Model
The EEC Model
promotes an education approach that develops workforce skills in line with modern, “demand-driven” education principles. It aims to enhance human capital
and produce manpower that meets the needs of industry sectors — an essential factor in fostering investment within the EEC area. This approach creates opportunities
for young people to graduate with the right competencies, secure suitable employment, and attain sustainable, well-paid careers.
promotes an education approach that develops workforce skills in line with modern, “demand-driven” education principles. It aims to enhance human capital and produce manpower that meets the needs of industry sectors — an essential factor in fostering investment within the EEC area. This approach creates opportunities for young people to graduate with the right competencies, secure suitable employment, and attain sustainable, well-paid careers.
Human capital development under the EEC Model is divided into three categories:

This pathway offers degree-level programs or vocational certificates
(Vocational Certificate/Higher Vocational Certificate),
jointly developed by educational institutions and industry partners. Students study free of charge, are guaranteed employment,
and receive attractive income opportunities, with private-sector support provided through scholarships
throughout the entire program.
This pathway offers degree-level programs or vocational certificates (Vocational Certificate/Higher Vocational Certificate), jointly developed by educational institutions and industry partners. Students study free of charge, are guaranteed employment, and receive attractive income opportunities, with private-sector support provided through scholarships throughout the entire program.

This category consists of short-term training programs designed
to urgently upgrade or reskill the workforce.
The government subsidizes up to 50% of the training costs,
while the private sector covers the remainder
and is eligible to claim a 2.5-times tax deduction
as an incentive to encourage investment
in human resource development.
This category consists of short-term training programs designed to urgently upgrade or reskill the workforce. The government subsidizes up to 50% of the training costs, while the private sector covers the remainder and is eligible
to claim a 2.5-times tax deduction as an incentive to encourage investment in human resource development.

This pathway focuses on upgrading competencies for
the transition to next-generation technologies, including
Automation Transformation (AX), Digital Transformation (DX),
and Green Transformation (GX). The target group includes
engineering or technical graduates who have been unemployed
for no longer than six months and are under 30 years of age.
Pilot courses include Semiconductor, Automation,
and EV-related programs.
Participants who complete the training are registered
as job-ready candidates. Investors or employers who hire these
registered trainees will be refunded 100% of the training costs
by the Eastern Economic Corridor Office (EECO). This mechanism
ensures continuity in training and helps meet the future workforce
demands of investors operating in the EEC.
This pathway focuses on upgrading competencies for the transition to next-generation technologies, including Automation Transformation (AX), Digital Transformation (DX), and Green Transformation (GX). The target group includes engineering or technical graduates who have been unemployed for no longer
than six months and are under 30 years of age. Pilot courses include Semiconductor, Automation, and EV-related programs.
Participants who complete the training are registered as job-ready candidates. Investors or employers who hire these registered trainees will be refunded 100%
of the training costs by the Eastern Economic Corridor Office (EECO). This mechanism ensures continuity in training and helps meet the future workforce demands of investors operating in the EEC.
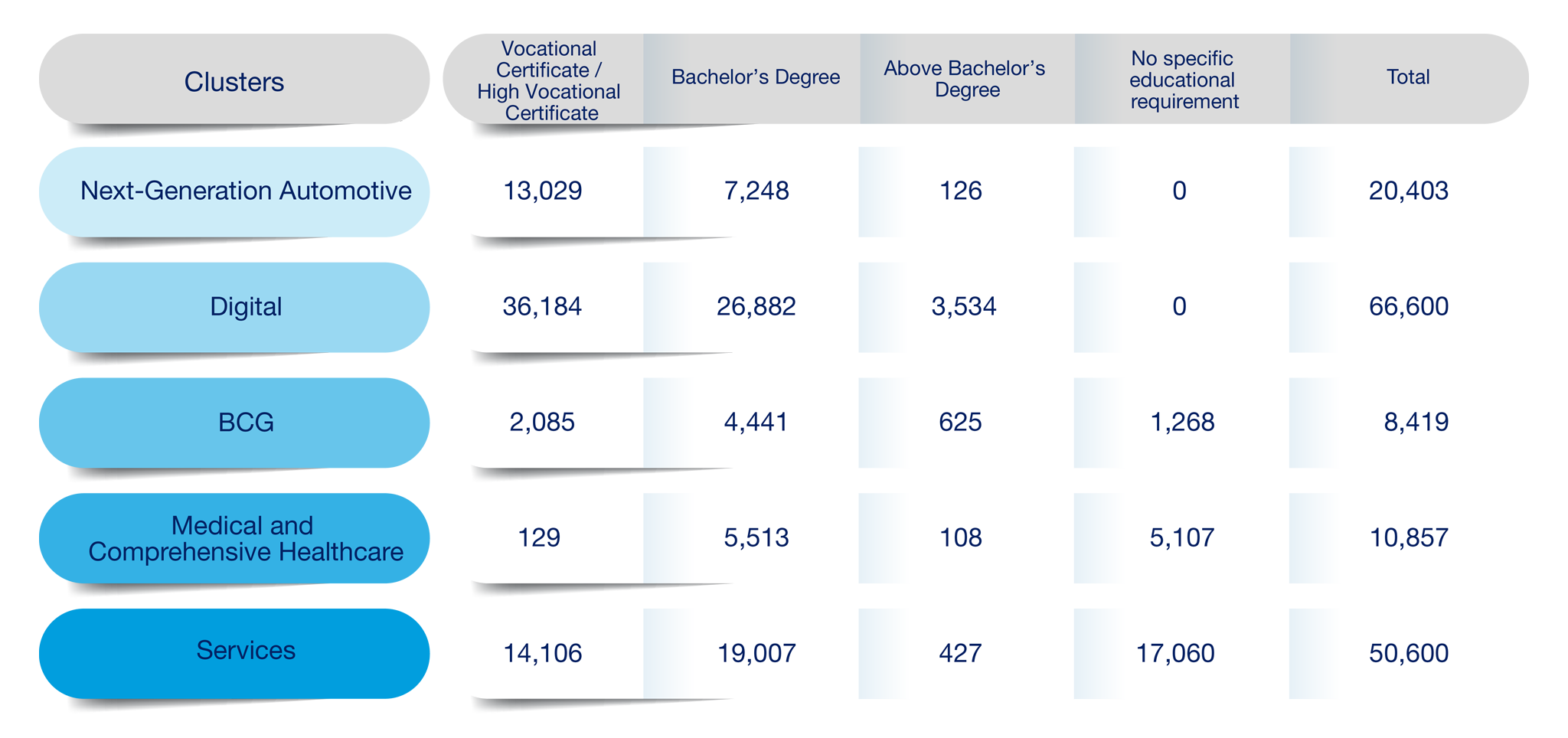
Total manpower demand for target industries in the EEC (2025–2029): 156,879 positions, disaggregated by industry as follows:

1. 1. Next-Generation Automotive
20,403 positions
No specific educational requirement: 0
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 13,029
Bachelor’s Degree: 7,248
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 126
2. Intelligent Electronics
43,198 positions
No specific educational requirement: 0
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 25,844
Bachelor’s Degree: 15,601
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 1,754

3. High-Value Tourism
10,232 positions
No specific educational requirement: 1,370
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 2,443
Bachelor’s Degree: 7,248
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 126

4. Food for the Future
520 positions
No specific educational requirement: 0
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 249
Bachelor’s Degree: 271
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 0

5. Automation and Robotics
16,043 positions
No specific educational requirement: 0
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 7,482
Bachelor’s Degree: 6,781
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 1,780

6. Aviation
7,053 positions
No specific educational requirement: 0
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 689
Bachelor’s Degree: 6,364
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 0

7. Biofuel and Biochemical
6,380 positions
No specific educational requirement: 0
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 1,619
Bachelor’s Degree: 4,160
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 602

8. Advanced Agriculture and Biotechnology
1,519 positions
No specific educational requirement: 1,268
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 217
Bachelor’s Degree: 10
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 24

9. Digital
7,358 positions
No specific educational requirement: 0
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 2,858
Bachelor’s Degree: 4,500
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 0

10. Medical and Comprehensive Healthcare
10,857 positions
No specific educational requirement: 5,107
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 129
Bachelor’s Degree: 5,513
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 108

11. Rail Systems
24,246 positions
No specific educational requirement: 15,690
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 4,899
Bachelor’s Degree: 3,232
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 427

12. Maritime Commerce
6,700 positions
No specific educational requirement: 0
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 4,836
Bachelor’s Degree: 1,864
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 0

13. Logistics
2,370 positions
No specific educational requirement: 0
Vocational Certificate / High Vocational Certificate: 1,239
Bachelor’s Degree: 1,131
Above Bachelor’s Degree: 2,370
Total manpower demand by cluster (2025–2029): 503,001 positions